This Robotic Arm Can Perform Surgery And 3D Print Inside The Human Body
This robotic arm could be useful in surgeries that require doctors to perform in hard-to-reach spots and may be inserted like an endoscope.
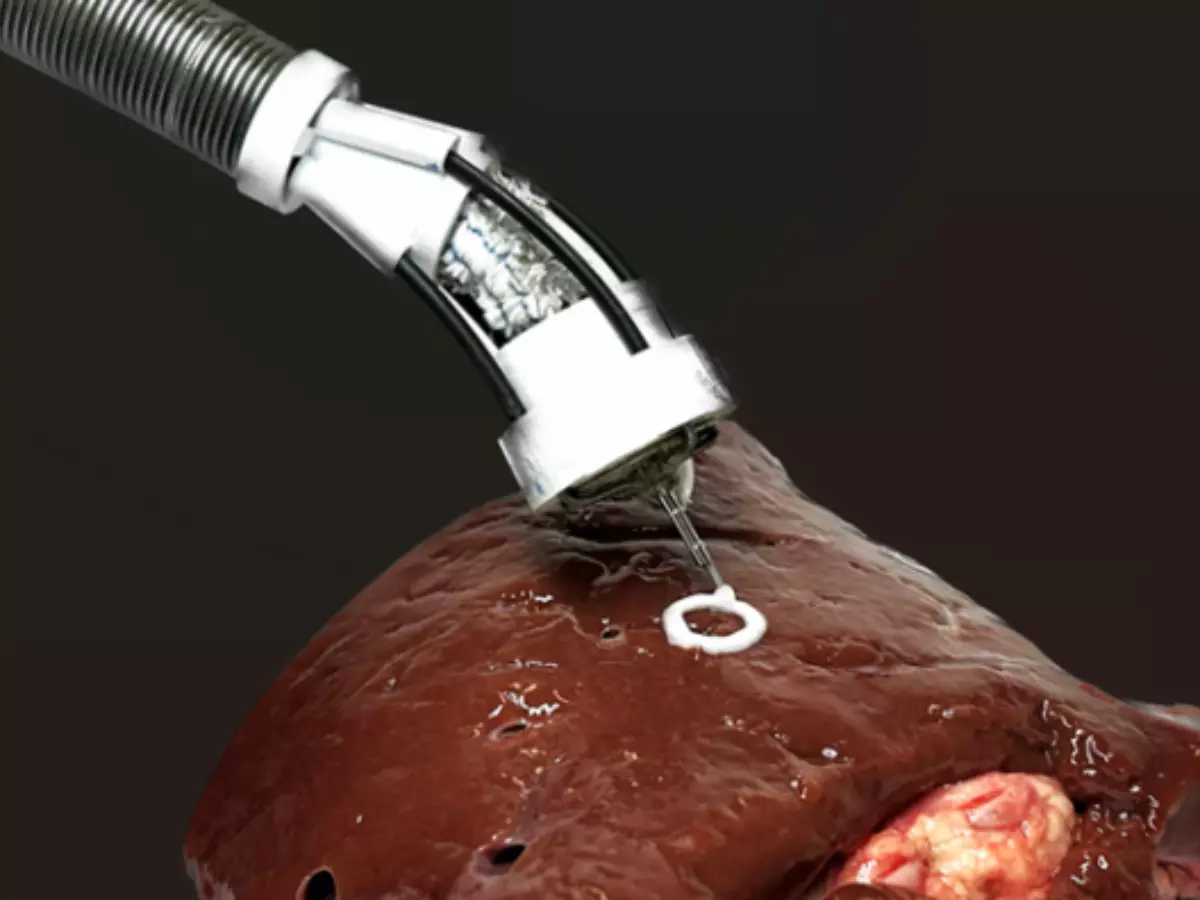
What if we told you that a robotic arm recently 3D-printed cells onto organs? Sounds bizarre, right? Scientists in Australia have done exactly this with a flexible soft robotic arm that 3D-prints cells onto organs.
This way, many risks associated with surgery may be eliminated, according to a beta version's description that may be found in the journal Advanced Science.
 Dr Thanh Do
Dr Thanh Do
"Our flexible 3D bioprinter means biomaterials can be directly delivered into the target tissue or organs with a minimally invasive approach," said Dr. Thanh Nho Do, lead researcher and a biomedical engineer at the University of New South Wales, in a press release.
This robotic arm could be useful in surgeries that require doctors to perform in hard-to-reach spots and may be inserted like an endoscope.
Why is this device revolutionary?
Its creators say that this robotic arm has the potential to eliminate many dangers usually associated with contemporary 3D printing techniques that "require biomaterials to be made outside the body."
"Implanting that into a person would usually require large open-field open surgery, which increases infection risks," Do added.
In addition, the press release states that this revolutionary tech can mitigate "mismatches between 3D-printed biomaterials and target tissues/organs" while also avoiding structural damage during transit.
Also read: Watch This Spider-Like Flying Robot Take Off With Its 16 Thrusters
For now, scientists have managed to successfully test the device in an artificial colon. Besides being able to 3D print on organs, the bot can also cut off cancerous lesions, clean blood, and excess tissue from the site of surgery - all of which was tested on a pig's intestine.
 UNSW
UNSW
Think that's all? Not quite! It appears that the robotic arm can also improve the rate of healing via a biomaterial.
"The developed F3DB was designed as an all-in-one endoscopic tool that avoids the use of changeable tools which are normally associated with longer procedural time and infection risks," Mai Thanh Thai, PhD student who collaborated on the study said.
Also read: Researchers Create AI Robot That Paints Art From Simple Text Prompts
Next, scientists want to imbibe a camera and scanner functionality into the device in order to print tissues in real time, according to SWNS.
What do you think about this amazing peice of tech? Let us know in the comments below. For more in the world of technology and science, keep reading Indiatimes.com.
