AI-Fuelled Xenobots Are Capable Of Reproduction: But What Is Their Purpose?
Xenobots were created using artificial intelligence and are capable of reproducing in the right settings. What can world's first reproduction capable robots do?
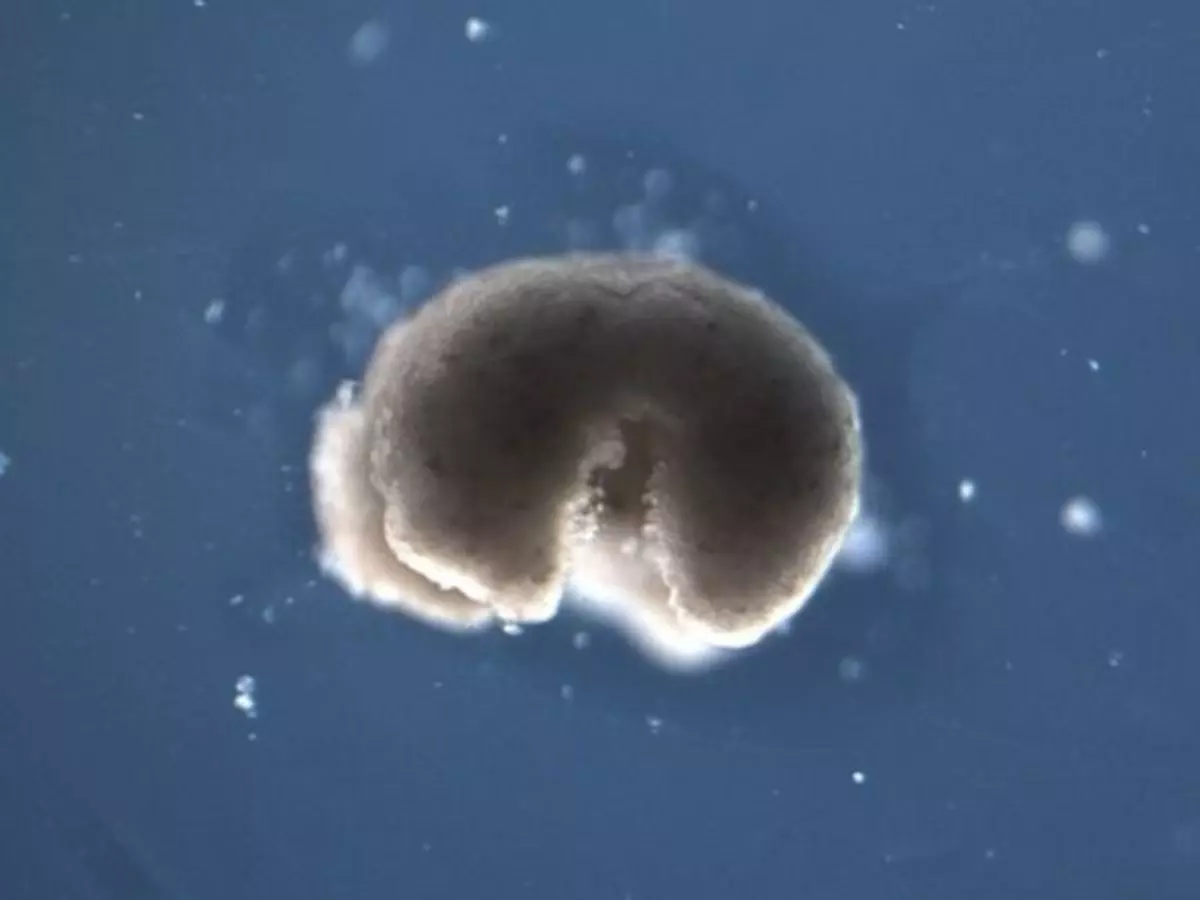
A groundbreaking feat recently occurred for artificial intelligence and robots alike when the first ever reproduction was witnessed in robots called "xenobots." Baby xenobots were created by a process called "kinetic replication" - a phenomenon never observed before but known to happen at the molecular level.
When you think of robots - we assume you picture futuristic steel figurines with wires that are modelled around human appearance and activities. Supported by software, such robots become "alive," if I may take the liberty to insinuate.
 Wikipedia
Wikipedia
But these xenobots are not your classic sci-fi cult film robots. They're extremely tiny and neither robot nor an animal. In fact, the best possible way to explain a xenobot is by calling it a "living, programmable organism."
What are xenobots made of?
Derived from stem cells of the African clawed frog, xenobots earlier displayed the ability to work in groups and to heal themselves.
The basic ingredient of these xenobots are stem cells. Using artificial intelligence, the xenobots were turned into c-shape (think of PacMan) robots. When put into a petri dish, the c-shaped xenobots were able to gather hundreds of tiny stem cells inside its mouth... creating new xenobots a few days later.
Also read: Xenobot Babies: World's First Living Robots Can Now Reproduce, Thanks To AI
While it is now common knowledge that the world's first robot reproduction has taken place through xenobots, there is still a lot of debate surrounding the purpose of these xenobots.
What is the purpose of xenobots?
In general, xenobots are used to study how cells cooperate to build complex bodies. The primary characteristic of xenobots is to corral a group of cells and to confine them. By the same logic, xenobots could be used in a variety of settings.
Douglas Blackiston, who built the xenobots told NPR that "if we could program these better, maybe they can selectively pick up and move specific cell types that we want or help us shape something that we're building in a dish for regenerative medicine."
 CNN/Douglas Blackiston & Sam Kriegman
CNN/Douglas Blackiston & Sam Kriegman
By extrapolating their ability to corral cells into a spot, perhaps xenobots could be used to clean microplastics in the ocean, as suspected by many.
In the medical field, advanced xenobots could be used to create patient specific cells that deliver drugs wherever intended, bypassing the challenges associated with other ways to deliver cells that sometimes cause issues with the immune response.
Also read: Watch: Video Shows Humanoid Robot With Scarily Realistic Facial Expressions
Even then, it appears that scientists still don't know what applications xenobots could be put to.
For Sam Kriegman, who developed the artificial intelligence (AI) programme responsible for creating xenobots, this creation shows "maybe life is more expected than unexpected."
 Douglas Blackiston & Sam Kriegman/ CNN
Douglas Blackiston & Sam Kriegman/ CNN
What do you think - should xenobots be studied further, especially considering they can't reproduce in independent settings? Or should we be scared of such robots that are more like living organisms than robots? Let us know in the comments below. For more in the world of science and tech, keep reading Indiatimes.com.
Citation
Hunt, K. C. (2021, November 29). World¡¯s first living robots can now reproduce, scientists say. CNN.
NPR (2021). Living robots made in a lab have found a new way to self-replicate, researchers say.
