China Approves Sinopharm Vaccine: It Uses Inactive SARS-CoV2 To Develop Immunity
The vaccine developed by Sinopharm is actually making use of inactivated SARS CoV-2 in the vaccine, to generate immunity and prevent the body against further infections
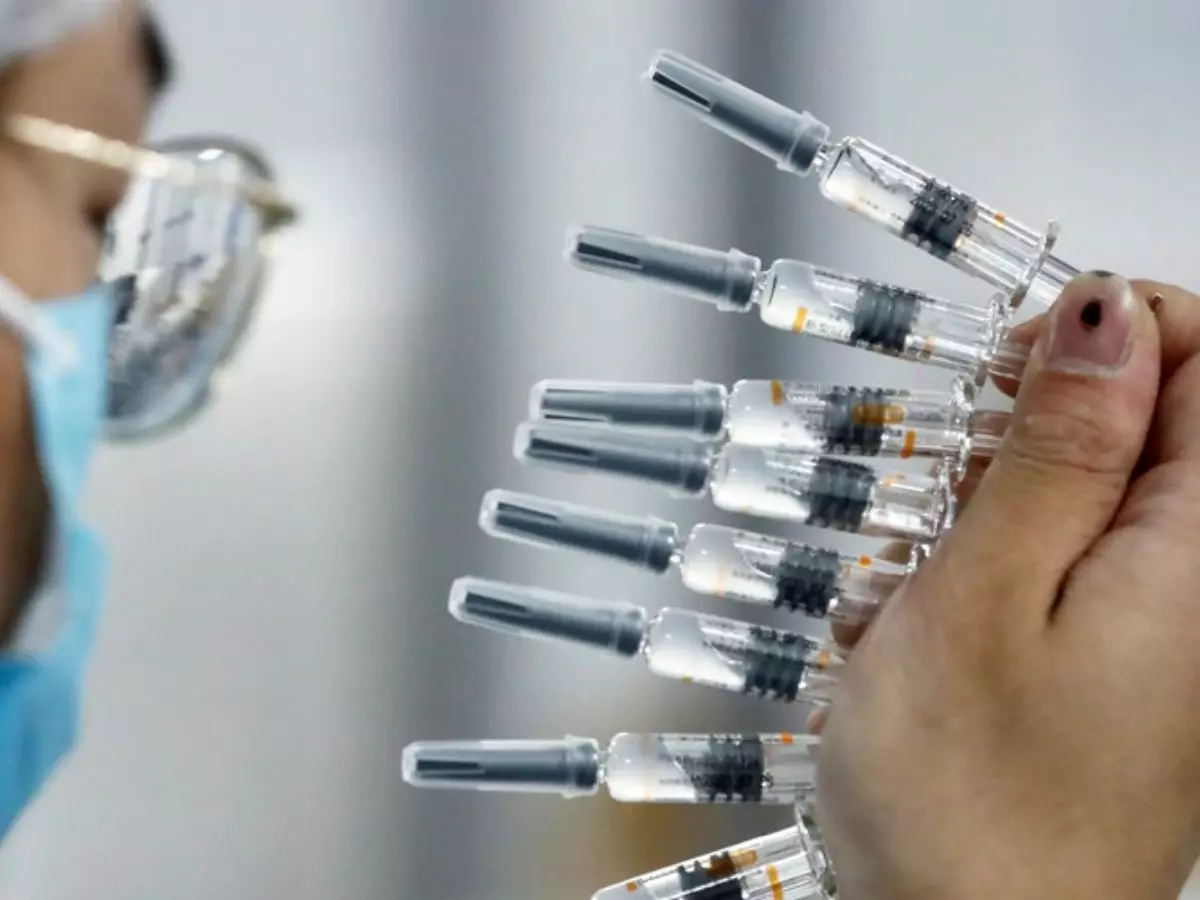
China today has gone ahead and announced its first-ever approval of a COVID-19 vaccine for general use in public -- a shot developed by state-backed Chinese pharmaceutical giant Sinopharm.
 Reuters
Reuters
Reported first by Reuters, as of now, the company hasn¡¯t revealed any data pertaining to its trials and the effectiveness of the vaccine against the novel coronavirus. However, the developer Beijing Biological Products Institute -- a part of Sinopharm¡¯s subsidiary China National Biotec Group revealed in a press release on Wednesday that the vaccine is 79.34 percent effective against the novel coronavirus, based on interim data.
Sure, all this might not sound as impressive as the competition with vaccines from Pfizer, Moderna and even Oxford-AstraZeneca offering over 90 percent effectiveness against the novel coronavirus, what¡¯s impressive is the tech behind it.
The vaccine uses Inactive/Weakened SARS CoV-2 Virus
The vaccine developed by Sinopharm is actually making use of inactivated SARS CoV-2 in the vaccine, to generate immunity and prevent the body against further infections. While it is not surprising for vaccine makers to adopt an inactive or weakened strain of the virus in the vaccine to develop immunity (we¡¯ve seen this with Polio and Measles vaccines), this is the first vaccine that is using this technique for the novel coronavirus.
 Reuters
Reuters
Different than the tech behind other leading vaccines
Vaccines like Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech are working on mRNA tech whereupon injection, a person receives genetic material (or mRNA) that encodes the viral protein. When these genetic instructions are injected, muscle cells train them to make the viral protein directly in the body.
The vaccine mRNA codes only for the critical fragment of the viral protein. This gives the immune system an idea of what the real virus could be like without actually causing disease while giving the immune system time to form powerful antibodies to take down the virus.
On the other hand, the vaccine developed by Oxford-AstraZeneca -- ChAdOx1 is an adenovirus vaccine, which basically has been developed from a viral vector based on a weakened version of the common cold (adenovirus) that also consists of the genetic material of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein.
 Reuters
Reuters
How does Sinopharm vaccine work?
According to an infographic shared by AFP, Sinopharm¡¯s vaccine uses either an inactivated form or a weakened form of SARS CoV-2. While the former replicates harmlessly, the latter doesn¡¯t replicate. Both result in the generation of spike protein or antigen. This is then investigated by the APC or Antigen Presenting Cell. APC also identifies peptide snippets of antigen.
These snippets then recognise the virus and then deploy their line of defence in the form of B cells and T cells. The former protects through antibodies that stop the virus infecting cells whereas the latter is responsible for destroying the infected cells.
Nations authorising the use of Sinopharm vaccine
While China might have just granted approval for use of the vaccine in its nation, the vaccine has already been approved for use in the United Arab Emirates, becoming the first foreign nation to approve a vaccine made in China. According to them, the vaccine was 86 percent effective as per interim results of Phase 3 trials.
 Reuters
Reuters
However, the same cannot be said for other nations as several countries don¡¯t put the same faith in the vaccine due to lack of transparency on results and the tech behind the vaccine.
