Drinking Too Much Alcohol? This Wearable Sensor Tells You When It's Time To Stop
According to the researchers, the results were adequate at least and in some cases excellent. The study was however not able to derive automated rules for alcohol detection.
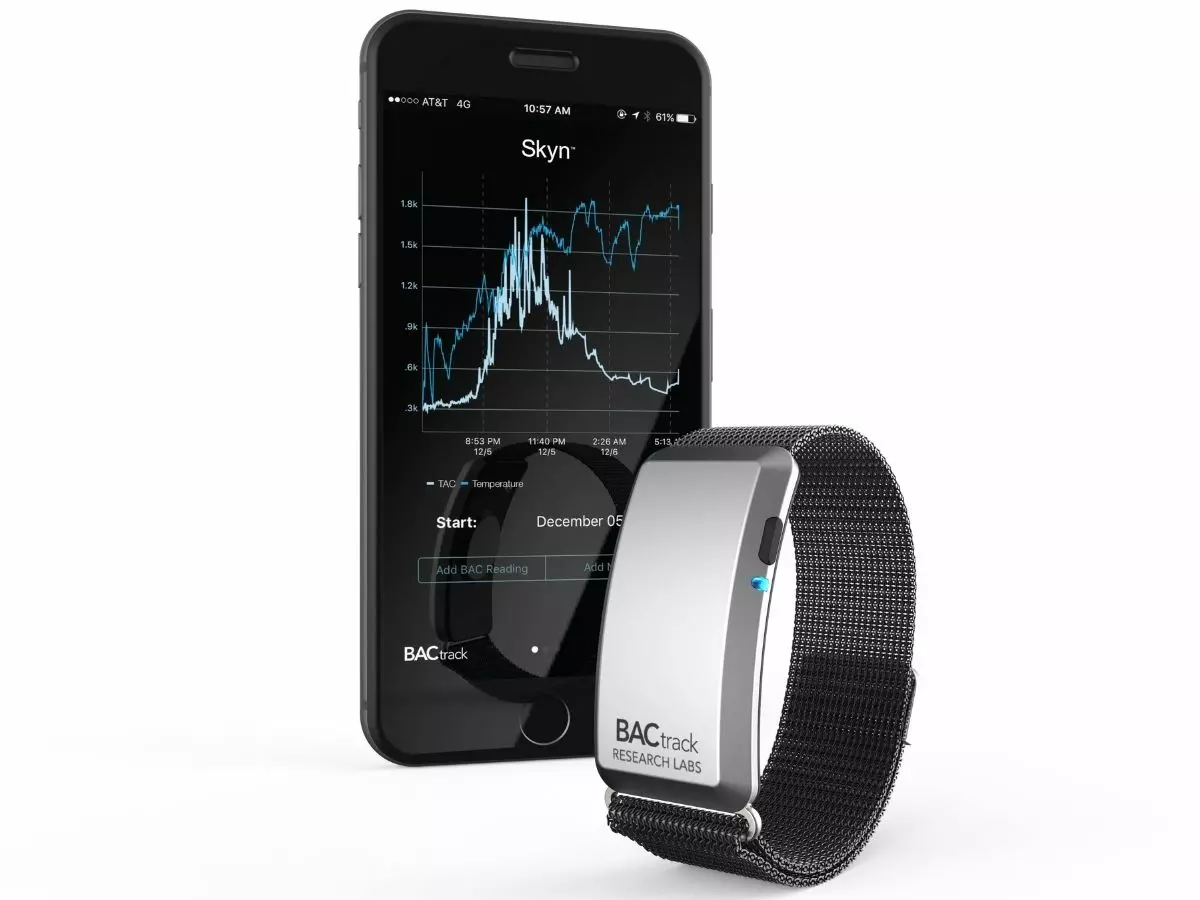
A new wearable sensor could help social drinkers make sure they don¡¯t drink too much and help them control their alcohol intake, reveals a novel report by The Independent.
 BACTrack
BACTrack
Also Read: Drinking Any Amount Of Alcohol Can Damage Your Brain, Claims Study
Developed by researchers from the Yale School of Medicine, the transdermal alcohol content sensors that actually measure ethanol excreted from the skin.
The sensors have originally been in use by the criminal justice system for monitoring abstinence. However, researchers claim that these sensors actually have the potential to motivate and support alcohol self-management.
According to the researchers, these sensors must be accurate and be capable of detecting alcohol with minimal delay post-drinking while also being feasible and convenient to wear.
Conventionally, they've been known to be bulky and worn on the ankles. Moreover, they're loud with their vibration capable of disrupting day-to-day activities. There are other sensor variants but they haven¡¯t been thoroughly tested under real-world situations.
The novel study looked at a field-based assessment of heavy drinking young adults to determine the accuracy and acceptability of a new sensor dubbed BACtrack Skyn and compared it with the conventional ankle-worn one. The study involved 47 participants from the age group of 18 to 25 who were asked to wear both the sensors for one to six days and consume alcohol as they normally would.
 Unsplash
Unsplash
Also Read: Drinking Two Beers A Day Damages Brain As Much As Ten Years Of Aging
Researchers saw that the new device was seen as a more accepted alternative measurement tool, especially when compared to using an app or a diary to monitor alcohol intake.
The novel device was also less disrupted by other day-to-day activities like sleeping, exercise etc.
According to the researchers, the results were adequate at least and in some cases excellent. The study was however not able to derive automated rules for alcohol detection. They said that the level of TAC corresponding to drinking was different among participants that enrolled during the first versus second half of the study.
They say it requires further analysis and development to make the device more user friendly for mass adoption. For more in the world of technology and science, keep reading Indiatimes.com.
