Trippiest Pic Of Jupiter Shows Huge Cyclones As Swirls, Thanks To NASA's Juno
NASA has released an extreme false color rendering of an image of the Jupiter cyclones from its Juno mission. In the image these cyclones can be seen as swirls of striking colors on the planet making a beautiful masterpiece. The composite image was made by citizen scientist Gerald Eichst?dt using data from the Juno spacecraft.
NASA¡¯s Juno space orbiter has been keeping an eye on Jupiter since 2016, meaning to unravel the mysteries around the planet¡¯s atmosphere, surface as well as its gravitational and magnetic fields.
In a new image, the US space agency shows a striking colour rendition of the persistent cyclones at Jupiter¡¯s north pole.
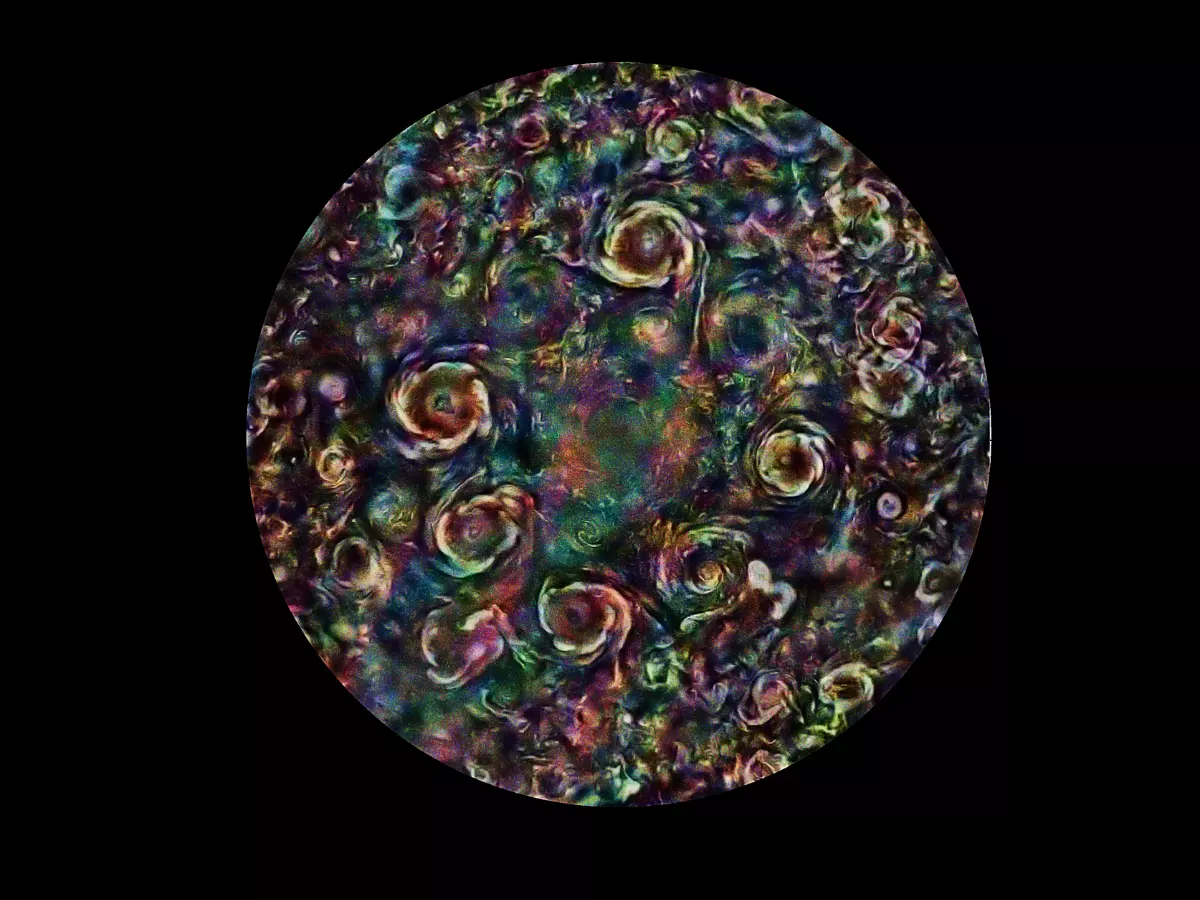
 Extreme false color rendering of an image from NASA¡¯s Juno mission (Image: NASA)
Extreme false color rendering of an image from NASA¡¯s Juno mission (Image: NASA)
Unlike anything you've seen before, NASA has released an extreme false color rendering of an image of the Jupiter cyclones from its Juno mission. In the image, these cyclones can be seen as swirls of striking colors on the planet, making a beautiful masterpiece that depicts the wonders of outer space in a scientific appearance.
The composite image was made by citizen scientist Gerald Eichst?dt using data from the Juno spacecraft. This data was recorded by the JunoCam instrument aboard the spacecraft during one of its four close passes by Jupiter. This one took place between February 17, 2020, and July 25, 2020.
The image is not the way the cyclones on Jupiter look in real life. Instead, the exaggerated colours are in part, a result of combining many individual images to create this view, says NASA in a recent release.
Jupiter cyclones through Juno Mission
What we see at the centre of the newly-released image is the ¡°huge, persistent cyclone¡± located at Jupiter¡¯s north pole. This primary cyclone is encircled by smaller cyclones, ranging in size from 2,500 to 2,900 miles (4,000 to 4,600 kilometers).
NASA says that the combined area covered by these cyclones is so huge that it would ¡°dwarf the Earth¡± in comparison.
 NASA Juno Spacecraft (Artist concept: NASA)
NASA Juno Spacecraft (Artist concept: NASA)
The image we see is a result of careful colour choices, in line with both ¡°the beauty of Jupiter¡± as well as the details present in Jupiter¡¯s dynamic cloud structure. NASA says that such compositions are made possible by the years of observations recorded by Juno, further helping the agency understand the dynamics of the largest planet in the solar system.
NASA claims that the Juno mission was able to capture the first clear views of Jupiter¡¯s polar regions. It further asserts that Juno¡¯s Jovian InfraRed Auroral Mapper (JIRAM) instrument has also mapped the area of the polar regions. In this wake, the spacecraft was able to map a similar pattern of storms at the planet¡¯s south pole as well.
