Nasal Vaccine To Cure Alzheimer's To Enter Human Trials For First Time
The vaccine is the brainchild of Howard L. Weiner, co-director of the centre that researches on neurological diseases at Brigham, who has been studying Alzheimer's disease for over 20 years
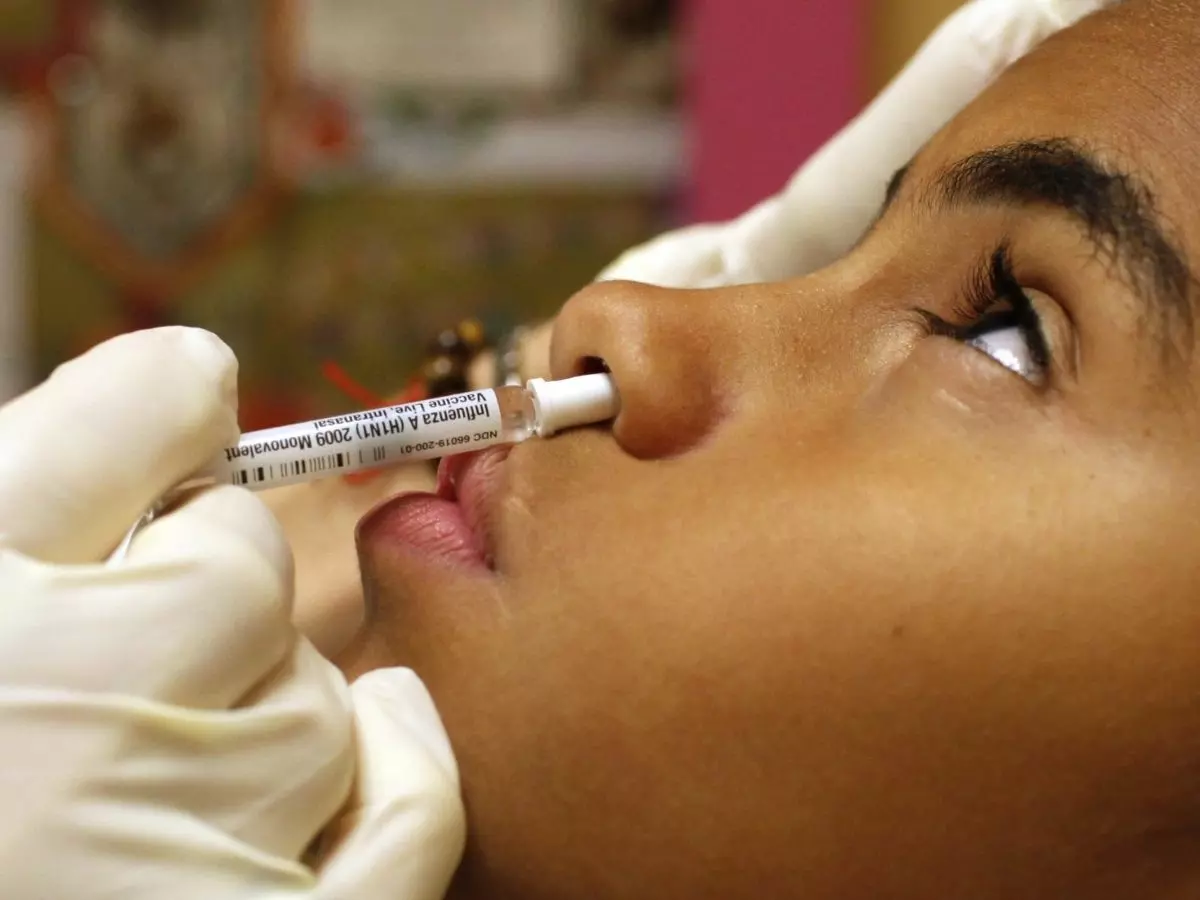
Humanity could be close to curing Alzheimer's, as a new nasal vaccine for preventing or slowing down of the aforementioned disease is undergoing human trials, according to a report by Insider.
 Reuters
Reuters
Also Read: What Causes Alzheimer's Disease? Scientists Finally Think They Have An Answer
The trials were announced last week by Brigham and Women's Hospital and it only involves a small number of volunteers -- 16 individuals from the age of 60 to 85 years who have preexisting Alzheimer's symptoms. They'll be given two doses of the vaccine, one week apart.
The vaccine is the brainchild of Howard L. Weiner, co-director of the centre that researches on neurological diseases at Brigham, who has been studying Alzheimer's disease for over 20 years.
The vaccine is based on decades of research that suggests that stimulating the immune system can clear out beta-amyloid plaques -- the culprit behind Alzheimer's. They normally form when pieces of the beta-amyloid collect between nerve cells that could hamper a person's ability to think or remember things.
Also Read: AI Predicts Onset Of Alzheimer's Disease With 99% Accuracy
 Unsplash
Unsplash
The vaccine spray, dubbed Protollin, acts as an immune modulator and is administered through the nasal passage in order to activate the immune cells -- specifically the white blood cells from the lymph node located in the neck area -- to get rid of the aforementioned plaque.
Also Read: Think Positive: Risk Of Dementia, Alzheimer's Disease Grows By Negative Thinking
While the concept isn't novel, a better understanding of the disease today makes it more promising.
The trial results will shed some light on the efficacy of the vaccine against the disease and its progression and based on that it can advance to larger trials involving more volunteers and eventual approval of the drug.
Keep reading Indiatimes.com for the latest science and technology news.
