Sweat Power: Scientists Build Tiny Strips To Generate Electricity From Your Sweat
The prototype device can generate electricity from the sweat that gets built up on your fingers and they claim that wearing it for 10 hours could generate enough power to run a watch for a good 24 hours.
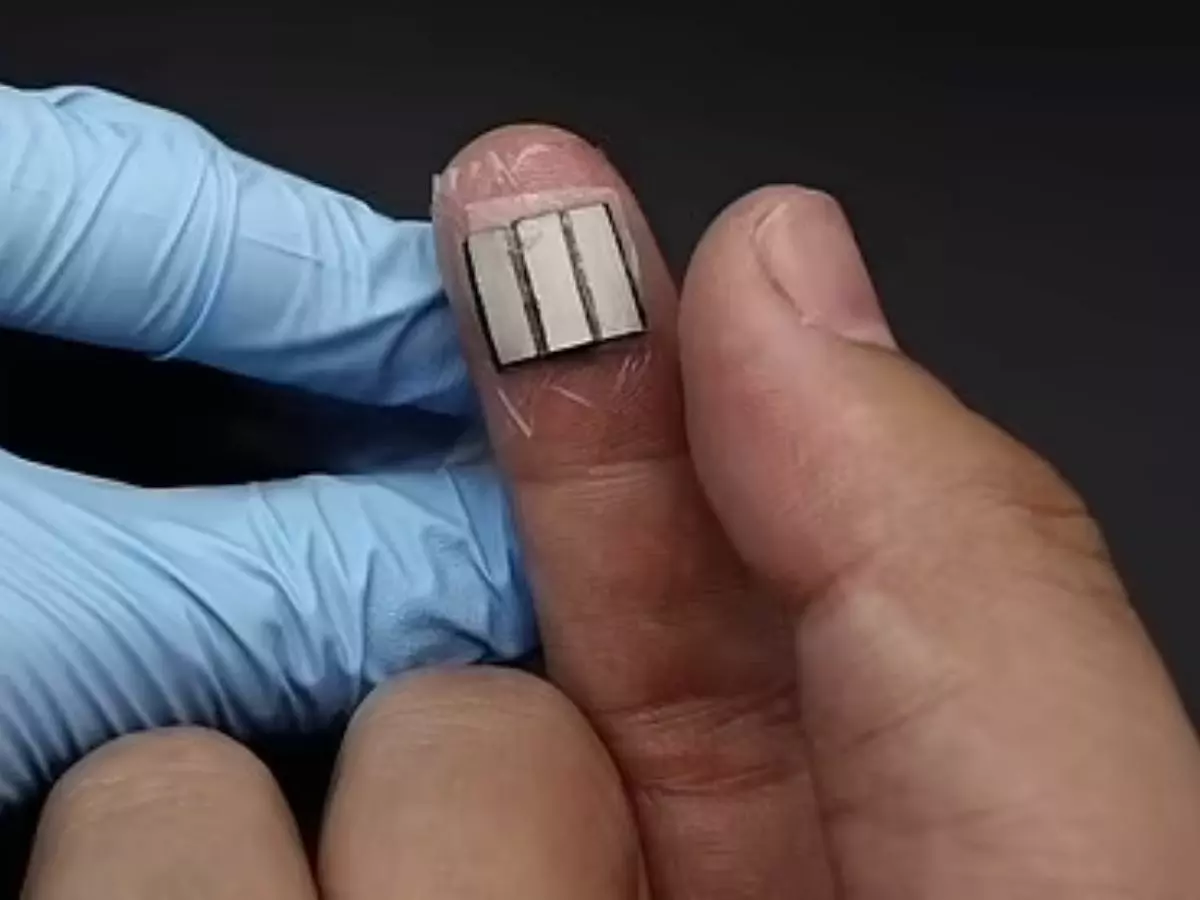
Researchers from the University of California, San Diego have developed a prototype device that can generate electricity from the sweat that gets built up on your fingers and they claim that wearing it for 10 hours could generate enough power to run a watch for a good 24 hours.
 Lu Yin
Lu Yin
Also Read: New Fabric Instantly Absorbs Sweat From Body And Turns It Into Electricity
Published in journal Joule, (reported first by Daily Mail) researchers highlight that our fingertips have the highest concentrations of sweat glands in the body -- each one of the glands produces 100 and 1000 times more perspiration than other areas of the body.
The way the prototype does this is by producing small amounts of electricity when the wearer of the device starts pressing surfaces, causing sweat formation. The device is loaded with electrical conductors made from a carbon foam that absorbs sweat from fingers. The enzymes on the electrode enable a chemical reaction between the sweat molecules of lactate and oxygen to generate electricity.
There is a small chip under the electrodes made from piezoelectric material that also generates power when it is pressed and stores it in a small capacitor to be discharged onto devices whenever needed.
Co-first author doctoral student Lu Yin explains, ¡°The size of the device is about one centimetre squared. Its material is flexible as well, so you don't need to worry about it being too rigid or feeling weird. You can comfortably wear it for an extended period of time.¡±
For testing this out, a test subject was asked to perform various tasks while wearing it on their finger that involved typing, tapping and even sleeping.
Also Read: New Material Inspired From Camel Keeps Perishable Food Cool Without Electricity
In the 10 hours of sleeping duration, the device managed to generate 400 millijoules of energy which is enough to power an electric wristwatch for a whole day. On the other hand, an hour of casual typing and clicking on a mouse enabled the device to collect around 30 millijoules.
 Lu Yin
Lu Yin
Also Read: Scientists Make Cloth That Can Be Flipped Inside Out To Feel Warmer Or Colder
Yin added, ¡°Our goal is to make this a practical device,' adding that they wanted to show it wasn't just another cool thing that could generate small amounts of power. We can actually use the energy to power useful electronics such as sensors and displays.¡±
Yin stated that they¡¯re working on developing more efficient and durable energy collection systems. Moreover, they¡¯re also fusing it with other kinds of energy harvesters to create new kinds of self-powered devices.
